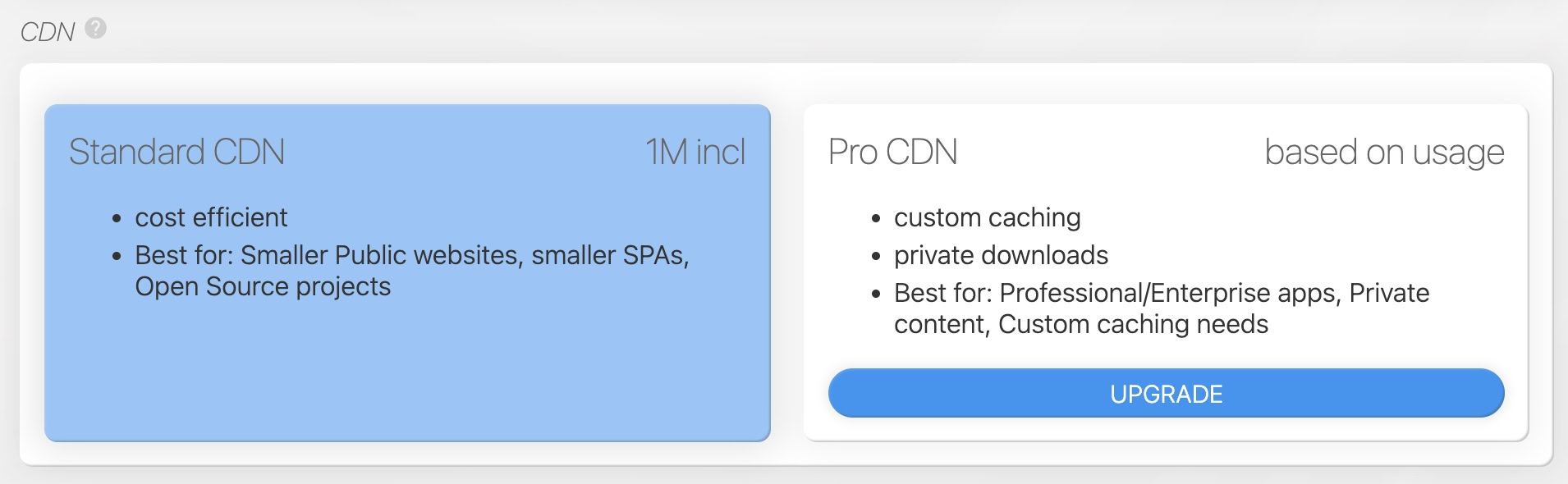
CDN types: Standard vs. Pro
Locize offers two different Content Delivery Network (CDN) infrastructures to serve your translation files. You can choose the one that best fits your project's security, caching, and feature requirements.
| Feature | Standard CDN (Default for new projects) | Pro CDN (Professional) |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Provider | BunnyCDN | AWS CloudFront |
| Cost Efficiency | For Free (for a very generous amount of monthly downloads) | On-Demand |
| Private Downloads | ❌ No (Public only) | ✅ Yes |
| Published Namespace History | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Custom Caching | ❌ Fixed (1 hour) | ✅ Customizable |
| Domains | api.lite.locize.app | api.locize.app |
| Best For | Smaller Public websites, smaller SPAs, Open Source projects | Professional/Enterprise apps, Private content, Custom caching needs |
Standard CDN (BunnyCDN)
The Standard CDN is the new default for all newly created projects. It is powered by BunnyCDN and provides a high-performance, cost-effective solution for most public-facing applications.
Key Characteristics
- Public Access Only: Translation files published to the Standard CDN are publicly accessible. You cannot restrict access using API keys or private publishing.
- Fixed Caching Policy: The caching duration (TTL) is fixed at 1 hour. You cannot define a custom
Cache-Controlmax-age. - No Native Published Namespace History: This CDN type does not support the Published Namespace History feature.
Development Workarounds for Caching
Since the default cache is 1 hour, you might see old translations during active development. You can bypass the cache using the following methods:
1. Using Query Parameters
Append ?cache=no to your fetch URL to force a fresh download:
https://api.lite.locize.app/{{projectId}}/{{version}}/{{lng}}/{{ns}}?cache=no2. Using i18next-locize-backend
If you are using the official backend plugin, set the reloadInterval or noCache option:
import i18next from "i18next";
import Locize from "i18next-locize-backend";
i18next.use(Locize).init({
backend: {
projectId: "[PROJECTID]",
cdnType: "standard",
noCache: true // <-- set strictly for development to bypass cache
},
fallbackLng: 'en',
supportedLngs: ['en', 'de']
});
// Alternative configuration:
// If 'debug: true' is set in i18next, it will also bypass the cache automatically
// even if noCache is not explicitly set.
/*
i18next.use(Locize).init({
debug: true,
backend: {
projectId: "[PROJECTID]",
cdnType: "standard"
},
// ... other options
});
*/Pro CDN (AWS CloudFront)
The Pro CDN is the robust infrastructure that Locize has used since the beginning. It is based on Amazon CloudFront and is designed for projects requiring advanced control, privacy, and safety nets.
Key Characteristics
- Private Downloads: Supports Private Publishing. You can restrict access to your translation files so they can only be downloaded with a valid API key.
- Custom Caching: You can fully configure the
Cache-Controlmax-age per version to optimize for latency or freshness according to your specific needs. - Published Namespace Backups: Automatically retains backups of your namespaces. This allows you to roll back to previous versions if a mistake is published.
Which one should I choose?
Choose Standard if:
- Your project is a smaller public website, landing page, or open-source project.
- Your translation data is not sensitive.
- You do not need to retain historical backups of translation files within the CDN.
- A 1-hour cache time is acceptable for your production environment.
Choose Pro if:
- Security is a priority: You need to ensure your translation files are not publicly downloadable (e.g., internal enterprise tools, unreleased products).
- Risk Management: You rely on Published Namespace Backups to restore data in case of accidental overwrites.
- Performance Tuning: You need granular control over browser caching (e.g., setting long cache times for production efficiency).
Changing your CDN Type
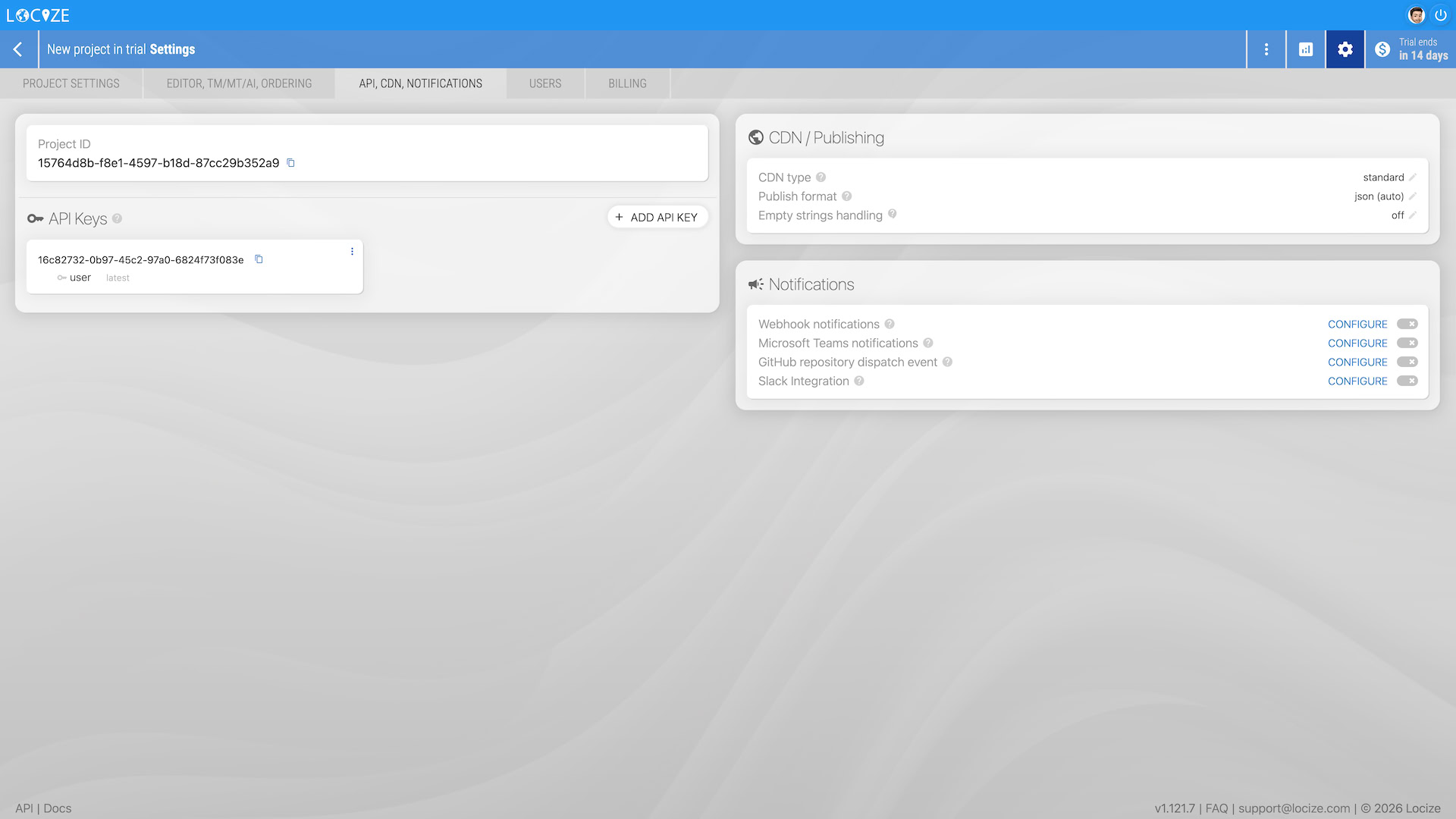
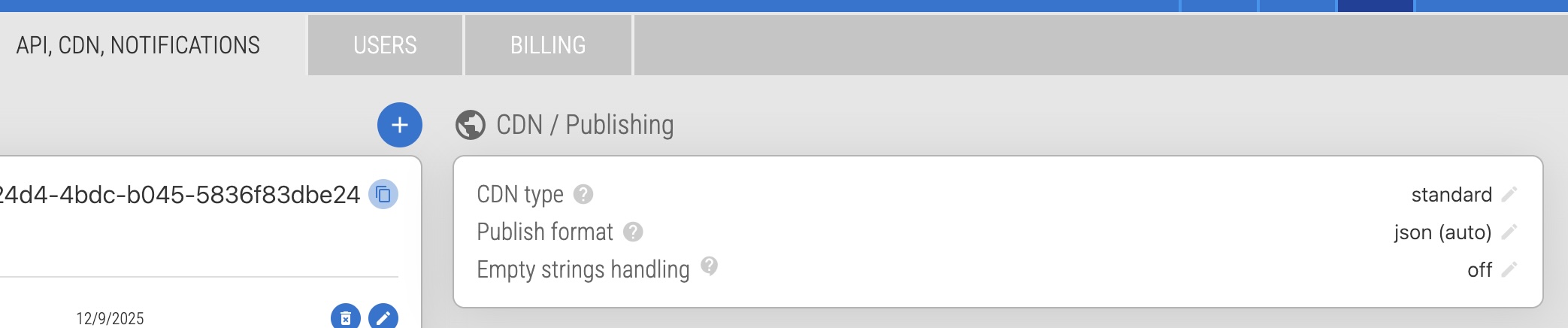
You can switch your project between Standard and Pro at any time in your project settings. During your trial you can change it on the "API, CDN, NOTIFICATIONS" tab:
And when subscribed you can change it on the "PLAN, ADDONS, ..." tab:
Depending on your integration you may need to change the
cdnTypeoption in your tools (CLI, i18next-locize-backend, locizify, locizer, etc.) or change the API endpoint.
