Checks/Issues
Locize helps you keep your translations high-quality and consistent by automatically performing a variety of checks. These checks identify potential issues, inconsistencies, and errors in your translations, making it easier to maintain accuracy and streamline your localization workflow.
On this page, you'll find an overview of possible issues, how to resolve them, and how to manage checks in the CAT (Computer-Assisted Translation) interface / Translation Editor.
How checks and issues are displayed
The CAT interface / Translation Editor will show warnings or errors on specific keys. For details, follow the link to the right-hand column for the selected key:

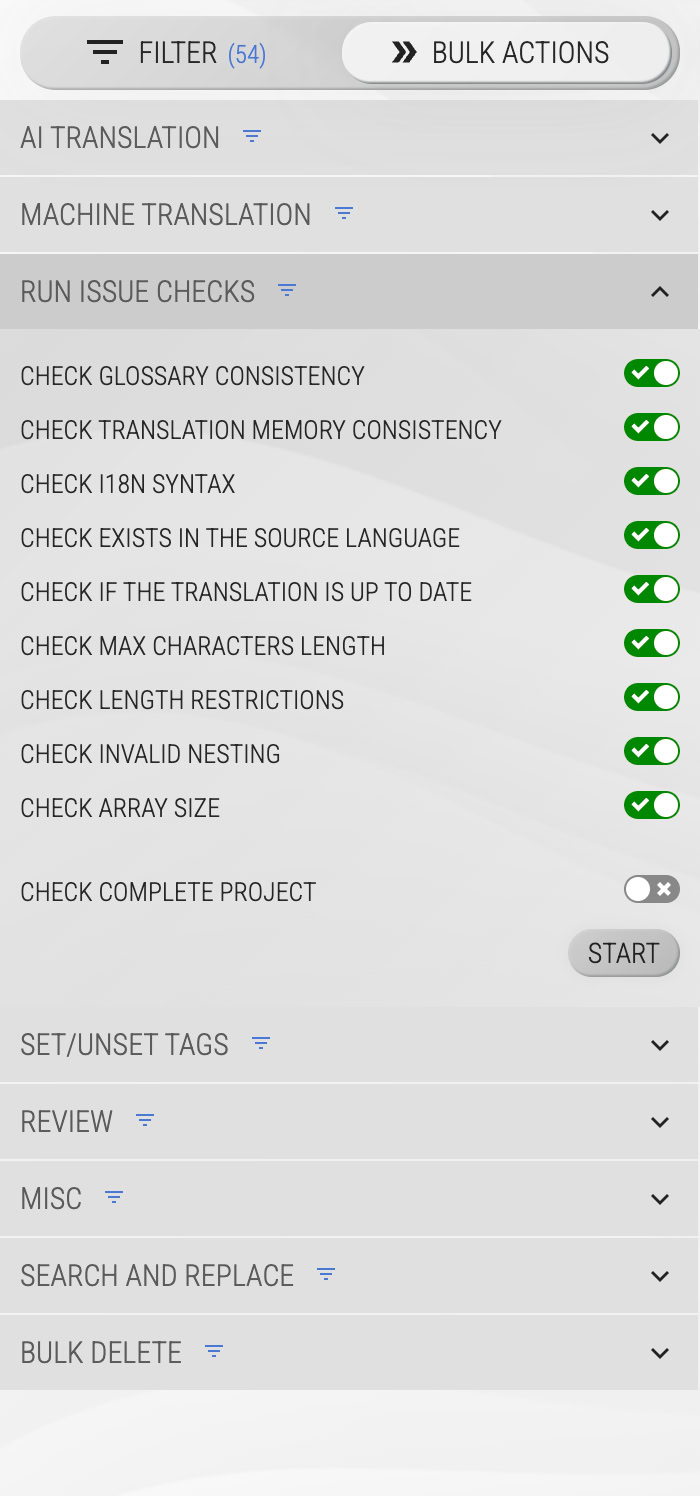
Running all checks for your project
You can run checks for a single segment on the right sidebar or for your entire project on the left side bar in the bulk actions:
In the bulk actions section, checks can be run for all segments or the currently filtered set. In the CAT interface / Translation Editor, checks run for the selected language and namespace.
Check this section in the video to see how Checks/Issues can be used.
checks/issues part of showcase/demo
Ignoring checks
If a check is not relevant, you can use the eye icon button to ignore an error for a specific segment.
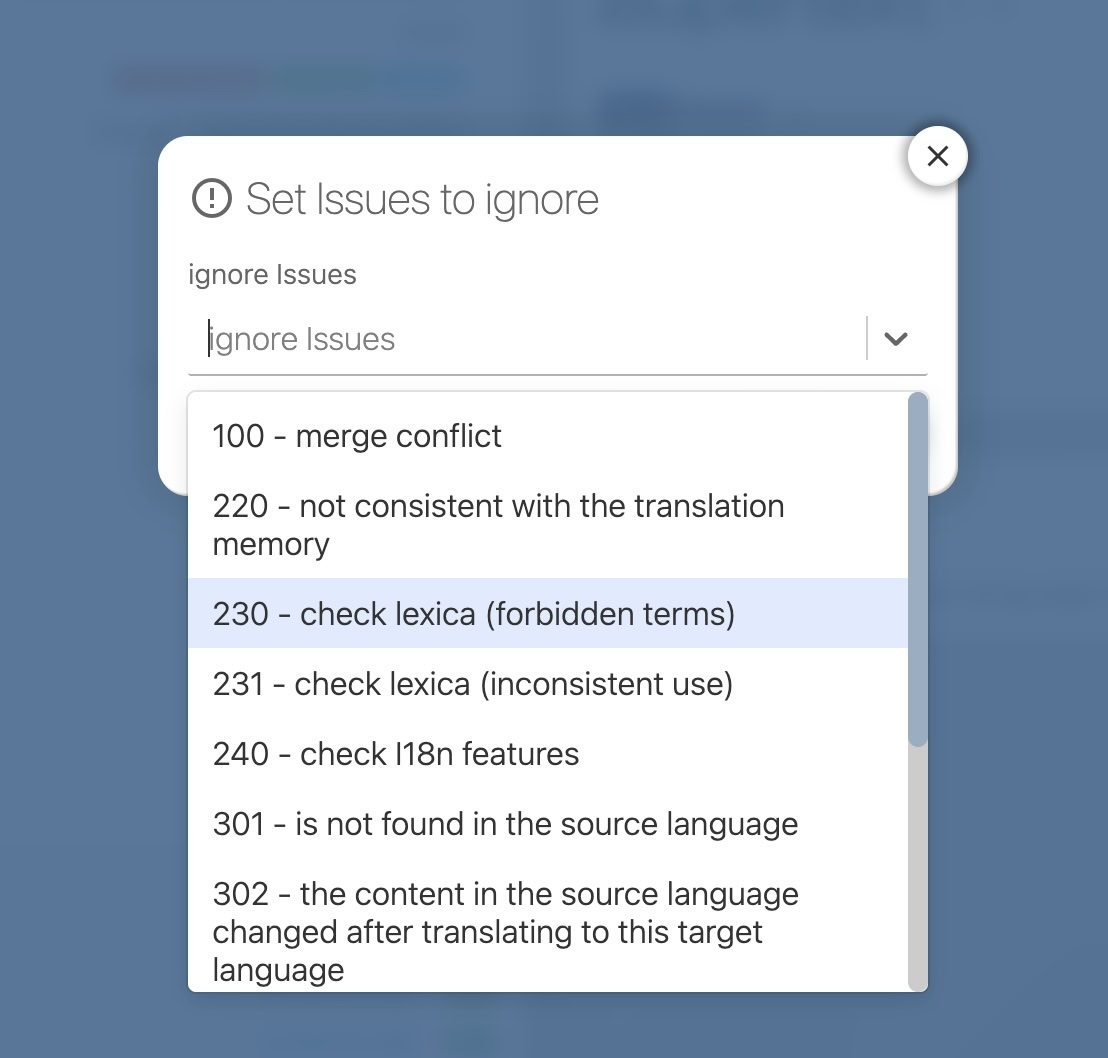
Generally ignoring checks
You can also generally ignore specific checks for your project. Go to your project settings, "EDITOR, TM/MT/AI, ORDERING" tab, and click the "Issues to ignore" section in the "Cat settings" card.
Consistency checks
Some checks, such as consistency checks, are performance-intensive and must be triggered manually.
Issue 220 - not consistent with the translation memory
This issue means another translation in the translation memory was translated differently. You can choose to update the translation for consistency or ignore the issue if the inconsistency is intentional.
Check glossary consistency
Glossary checks are also performance-intensive and must be triggered manually. They only work if you have uploaded a glossary file in your settings.
Issue 230 - found forbidden term (glossary)
The translation contains a term that is forbidden in your project's glossary.
Issue 231 - inconsistent terms (glossary)
The segment matches a glossary entry in the source language, but no allowed term was used in the target language.
Check i18n syntax consistency
This check compares source and target translations for matching i18n syntax features (such as interpolation, nesting, etc.).
Issue 240 - detected i18n syntax inconsistency
The translation contains a different number of i18n syntax elements compared to the source.
Miscellaneous checks
Check exists in the source language
Issue 301 - is not found in the source language
The key was only imported into a target language. It is recommended to add the content in the source language as well.
This may also affect your translation statistics and the percentage of translated segments.
Check if the translation is up to date
Issue 302 - the content in the source language changed after translating to this target language
There was a change to the source content. The translation might be outdated or incorrect. Check if the provided translation is still valid.
If the translation is still valid, you can confirm it:

Do not forget to click the SAVE button after clicking CONFIRM.
Check max characters length
issue 310 - is longer than the defined max characters
In the source language, a max length is defined for this sentence, and the provided translation is too long.
File checks
Invalid Nesting
issue 420 - gets nested into another string
This issue exists if there is a key eg. key.nested that would be nested into another key key. The result in a JSON export would then be:
{
"key": "value"
}
// or
{
"key": {
"nested": "value"
}
}So you would lose one of the keys in your export. To solve this issue rename one of the keys.
Check array size
issue 430 - check for array issue
The key is in form key.10001 which leads to exporting as an array (eg. in the JSON format). Having such a key would result in the creation of an array with the given number. This check asserts array sizes stay in a limited size (below 100).
You can avoid the conversion of the content to an array by providing a key that has a non-numeric end like key.aString.
